
About GERD
GERD has significant unmet medical needs
About GERD
Millions of people around the world suffer from Gastroesophageal reflux disease, GERD. Still, Standard of Care treatment, (SoC), PPI-based drugs, are not effective enough for all types of GERD. Heartburn is a common symptom and in severe stages, pain and other symptoms often occur.
What is reflux disease?
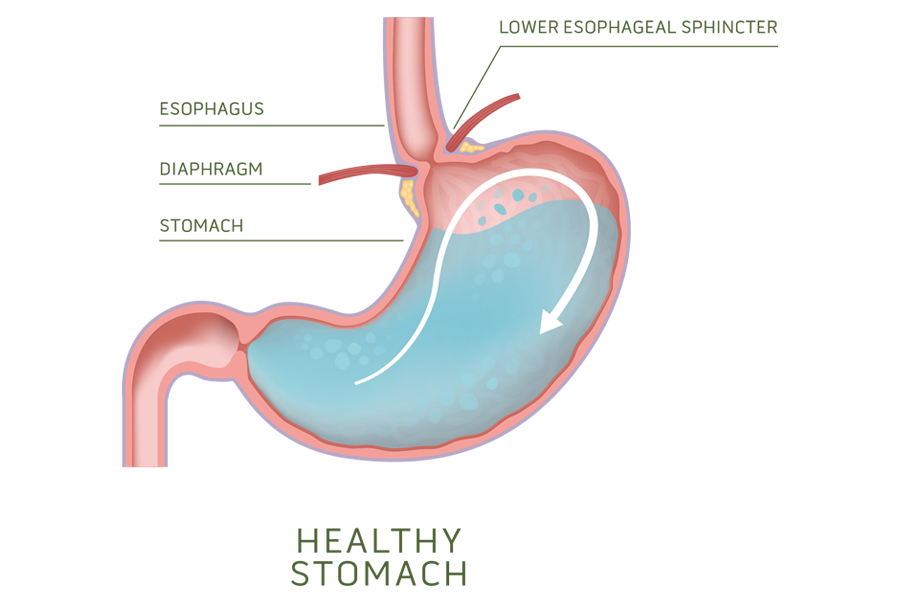
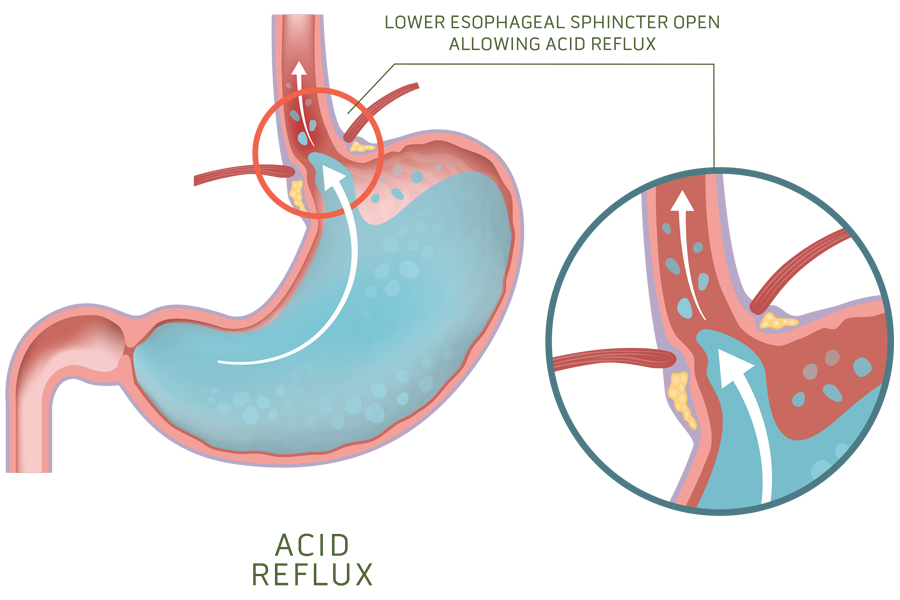
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or acid reflux, is a condition in which the content of the stomach regurgitates and backs up into the esophagus. The refluxate is usually acidic and often causes inflammation, erosions, and symptoms such as heartburn.
-
A disease caused by an incompetent valve with decreased ability to prevent gastric content to reflux into the esophagus.
-
Though GERD symptoms vary from person to person, chronic heartburn and acid regurgitation are the most common symptoms.
Why does the disease occur?
-
GERD occurs when the esophageal defense mechanisms are overwhelmed by gastric contents that reflux into the esophagus
-
Relocation of the upper part of the stomach above the diaphragm, i.e., hiatal hernia, is a common indirect cause of GERD
-
Prevalence increases with age.
Stages of GERD

GERD can occur in different stages, from esophageal hypersensitivity to erosive GERD and additionally further complications as the disease progresses.
-
Reflux hypersensitivity
Reflux hypersensitivity is classified as a stage of GERD. It comes with typical heartburn symptoms associated with reflux events. No tissue is damaged. -
sGERD
Symptomatic non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease. sGERD is characterized by reflux symptoms without visible tissue damage. -
(eGERD)
Erosive GERD, esophagitis, is defined as the presence of tissue damage and erosions caused by stomach acid. -
Complicated GERD
Complicated GERD is defined as ulcers, strictures, or Barrett's esophagus.
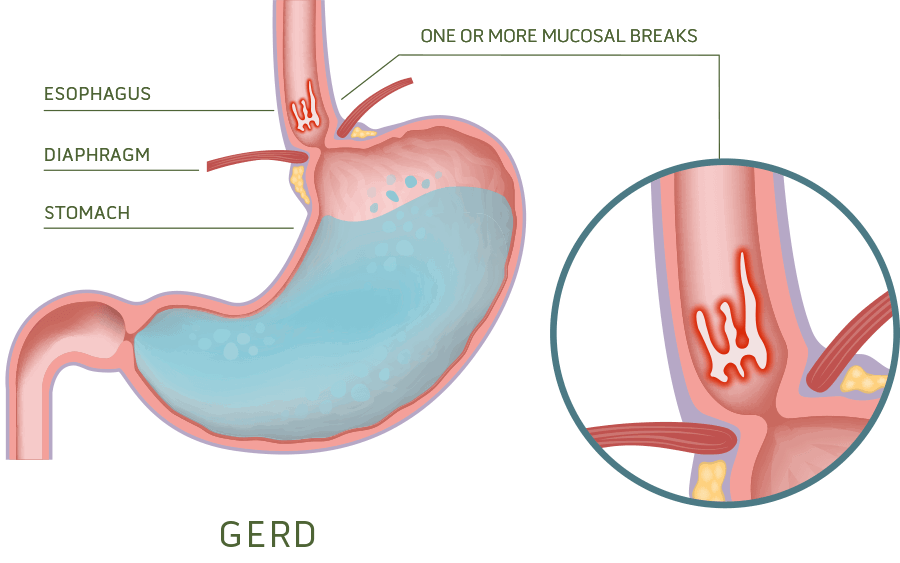
Los Angeles Classification of Reflux Esophagitis
The Los Angeles classification system of eGERD is a widely used system to describe the endoscopic appearance of reflux esophagitis and grade its severity.
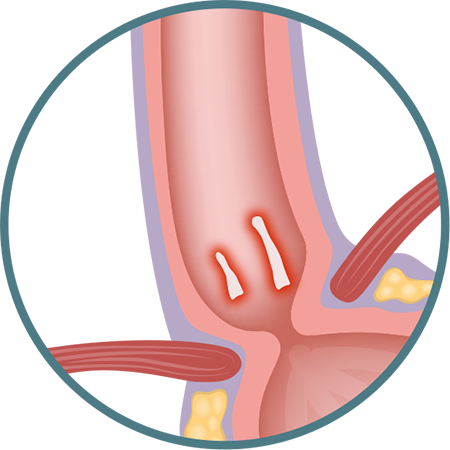
GRADE A
One (or more) mucosal break(s) no longer than 5 mm that does not extend between the tops of two mucosal folds.
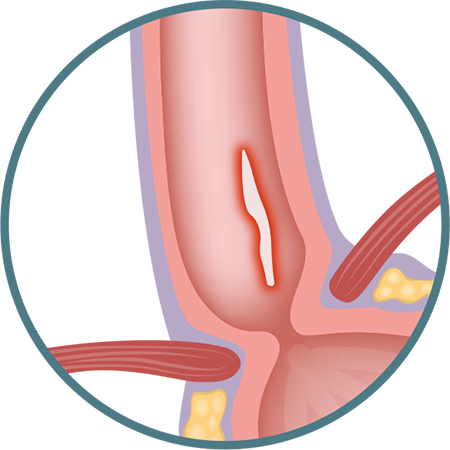
GRADE B
One (or more) mucosal break(s) more than 5 mm long that does not extend between the tops of two mucosal folds.
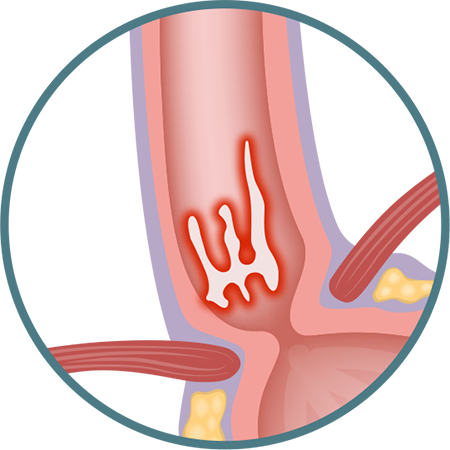
GRADE C
One (or more) mucosal break(s) that is continuous between the tops of two or more mucosal folds but involve(s) less than 75% of the oesophageal circumference.
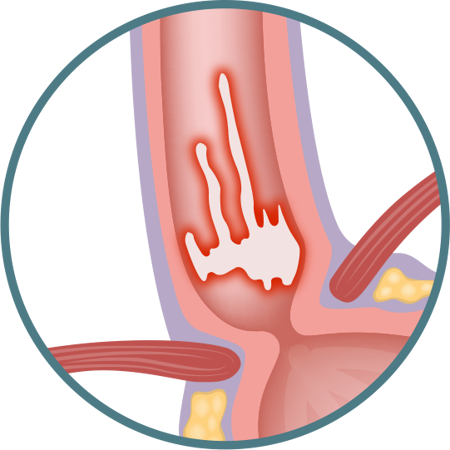
GRADE D
One (or more) mucosal break(s) which involve(s) at least 75% of the oesophageal circumference.
How do you manage the disease?
-
Erosions and symptoms require effective treatment.
-
Current standard of care primarily includes PPIs, e.g., Nexium, Takepron, Losec, etc.
-
Surgery is an option, especially for those with ”volume reflux,” a condition that has severe implications on quality of life.
What are the challenges with current standard treatment?
A substantial portion of patients suffering from GERD experience limited effects following standard-of-care treatment, representing the medical unmet need. A new solution is required for patients having insufficient treatment effects with current medication.
Facts
-
~1/3 of patients with eGERD grade C remain unhealed after four weeks with standard PPI therapy
-
More than 50% of patients with eGERD grade D remain unhealed after four weeks with standard PPI therapy
-
~10% of patients with eGERD grades A and B are unhealed after four weeks with standard PPI therapy
-
~85% of all eGERD patients suffer from nocturnal symptoms
Read more about life with GERD
Indication aspiration
Cinclus Pharma’s lead candidate, linaprazan glurate, addresses a significant unmet medical need with several millions of people worldwide. The main target groups are patients with moderate to severe GERD or Helicobacter Pylori (H.Pylori) infection, where available therapy is not effective enough.
Read more about linaprazan glurate



